 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator determines the power consumption of an AC circuit, either single-phase or three-phase, based on voltage, current, and power factor.
Purpose: It helps users calculate the power requirements for electrical devices or systems, useful for electrical engineering, energy management, and equipment sizing.
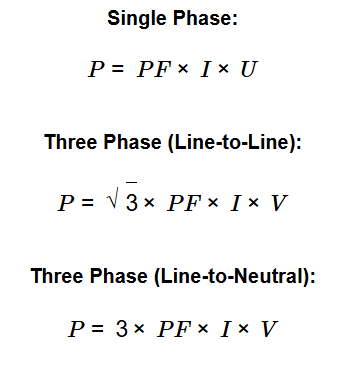
Power is calculated using the following formulas:
Steps:
Details: Accurate power calculation ensures proper sizing of electrical components, prevents overloading, and optimizes energy usage in AC systems.
Tips: Select the AC type. If you choose AC Single Phase, you’ll only need to enter voltage, current, and power factor. If you choose AC Three Phase, an additional option will appear to select Line-to-Line or Line-to-Neutral voltage. The result is the power in multiple units: mW, W, kW, MW, and GW.
Examples:
Q: What is the power factor?
A: Power factor (PF) is a measure of how effectively electrical power is converted into useful work, ranging from 0 to 1. A typical value is 0.8.
Q: What’s the difference between Line-to-Line and Line-to-Neutral?
A: Line-to-Line voltage is measured between two phases in a three-phase system, while Line-to-Neutral is measured between a phase and the neutral point. These options only appear when AC Three Phase is selected.
Q: Why are there different formulas for Three Phase?
A: The formulas account for the phase relationships in a three-phase system, with √3 for Line-to-Line due to the phase angle, and 3 for Line-to-Neutral as it considers all three phases.
Q: Why don’t I see Line-to-Line or Line-to-Neutral for Single Phase?
A: These options are specific to Three Phase systems, as Single Phase systems do not have multiple phases to measure between.
Q: Why are results shown in multiple units?
A: Displaying power in milliwatts (mW), watts (W), kilowatts (kW), megawatts (MW), and gigawatts (GW) provides flexibility for different applications, as some contexts may require smaller or larger units.