 Home
Home
 Back
Back
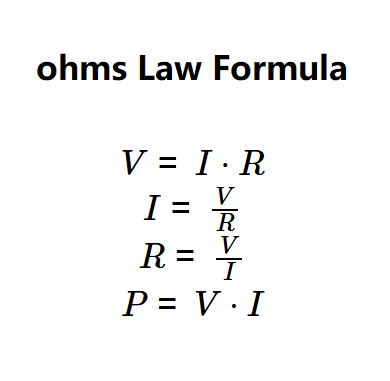
Definition: This calculator computes voltage (\( V \)), current (\( I \)), resistance (\( R \)), or power (\( P \)) in an electrical circuit using Ohm's Law and the power equation.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering and physics to analyze simple circuits, determine unknown parameters, and calculate power consumption.
The calculator uses the following equations:
Where:
Steps:
Details: Ohm's Law is fundamental in electrical engineering for designing and analyzing circuits, ensuring proper voltage, current, and resistance values, and calculating power consumption for devices.
Tips: Ensure all inputs are positive for resistance and current, and non-negative for voltage. The calculator assumes a simple linear circuit where Ohm's Law applies directly.
Examples:
Q: What is Ohm's Law?
A: Ohm's Law states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current through it, with the resistance as the constant of proportionality: \( V = I \cdot R \).
Q: When does Ohm's Law apply?
A: Ohm's Law applies to linear circuits with constant resistance, such as simple resistors. It may not apply to non-linear components like diodes or capacitors.
Q: How is power related to Ohm's Law?
A: Power in a circuit can be calculated using the equation \( P = V \cdot I \), where \( V \) and \( I \) can be derived from Ohm's Law if needed.