Single phase Voltage Drop Calculator
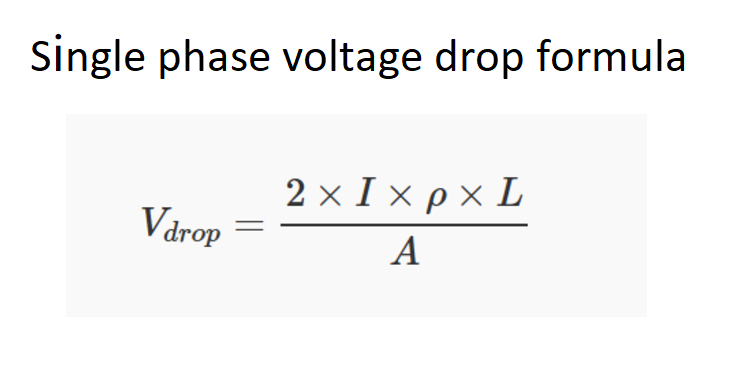
Understanding Voltage Drop
Voltage drop is the reduction in voltage in an electrical circuit between the source and load. It is important to minimize voltage drop to ensure efficient operation of electrical equipment.
Several factors affect voltage drop, including the length of the conductor, the cross-sectional area of the conductor, the material of the conductor, and the current flowing through the conductor.
Use the formula: $$V_{drop} = \frac{2 \cdot I \cdot \rho \cdot L}{A}$$ where \(I\) is the current, \(\rho\) is the resistivity of the material, \(L\) is the length of the conductor, and \(A\) is the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Common Questions
What is an acceptable voltage drop? Generally, a voltage drop of less than 3% is considered acceptable for most applications.
How can I reduce voltage drop? To reduce voltage drop, you can use conductors with larger cross-sectional areas, reduce the length of the conductors, or use materials with lower resistivity.
 Home
Home Back
Back