1. What is a Three-Phase Power Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the apparent power (S), active power (P), and reactive power (Q) in a three-phase circuit using either phase or line quantities and power factor.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to analyze power in three-phase systems, common in industrial and commercial power distribution.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
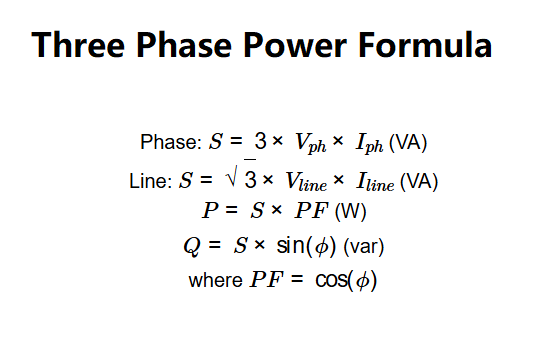
Phase: \( S = 3 \times V_{ph} \times I_{ph} \) (VA)
Line: \( S = \sqrt{3} \times V_{line} \times I_{line} \) (VA)
\( P = S \times PF \) (W)
\( Q = S \times \sin(\phi) \) (var)
where \( PF = \cos(\phi) \)
Where:
- \( S \) is the apparent power (VA)
- \( P \) is the active power (W)
- \( Q \) is the reactive power (var)
- \( V_{ph} \), \( I_{ph} \) are phase voltage (V) and current (A)
- \( V_{line} \), \( I_{line} \) are line voltage (V) and current (A)
- \( PF \) is the power factor (0 to 1)
- \( \phi \) is the phase angle
Steps:
- Select input type (phase or line)
- Enter voltage, current, and power factor
- Convert inputs to base units (V, A)
- Calculate \( S \), \( P \), and \( Q \)
- Display results in multiple units
3. Importance of Three-Phase Power Calculation
Accurate power calculations ensure efficient design and operation of three-phase systems, optimizing energy use and load balancing.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Phase: \( V_{ph} = 230 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{ph} = 10 \, \text{A} \), \( PF = 0.8 \):
- \( S = 6900.000 \, \text{VA} \) / \( 6.900 \, \text{kVA} \) / \( 0.007 \, \text{MVA} \)
- \( P = 5520.000 \, \text{W} \) / \( 5.520 \, \text{kW} \) / \( 0.006 \, \text{MW} \)
- \( Q = 4140.000 \, \text{var} \) / \( 4.140 \, \text{kvar} \) / \( 0.004 \, \text{Mvar} \)
- Line: \( V_{line} = 400 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{line} = 10 \, \text{A} \), \( PF = 0.8 \):
- \( S = 6928.203 \, \text{VA} \) / \( 6.928 \, \text{kVA} \) / \( 0.007 \, \text{MVA} \)
- \( P = 5542.563 \, \text{W} \) / \( 5.543 \, \text{kW} \) / \( 0.006 \, \text{MW} \)
- \( Q = 4156.922 \, \text{var} \) / \( 4.157 \, \text{kvar} \) / \( 0.004 \, \text{Mvar} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What’s the difference between phase and line quantities?
A: Phase quantities (Vph, Iph) are per-phase values; line quantities (Vline, Iline) are between phases or total current, differing by \( \sqrt{3} \) in star/delta connections.
Q: Why is reactive power important?
A: Reactive power (Q) affects voltage stability and efficiency in AC systems, though it doesn’t perform useful work.
Three-Phase Power Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back