 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator converts voltage (V) and impedance (R) into dBm, a unit of power expressed in decibels relative to 1 milliwatt (mW).
Purpose: It is used in RF engineering, telecommunications, and electronics to express power levels in a logarithmic scale based on voltage and impedance measurements.
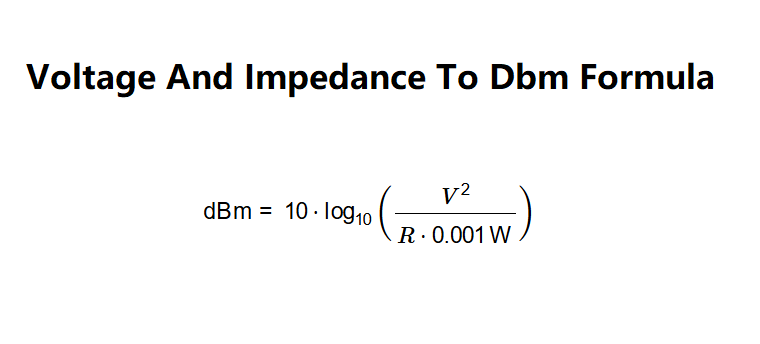
dBm is calculated using:
Voltage conversions:
Explanation: The input voltage is converted to volts, and the impedance is converted to ohms. The power in watts is calculated using \( P = \frac{V^2}{R} \), and then dBm is computed by comparing this power to the reference 1 mW (0.001 W) using the logarithmic formula.
Details: dBm is widely used in RF systems because it simplifies calculations involving power gains, losses, and signal levels, especially in antennas, amplifiers, and communication systems, when starting from voltage measurements.
Tips: Enter the voltage (V) in V, mV, or µV (voltage must be non-negative) and the impedance in Ω, kΩ, or MΩ (impedance must be greater than 0). The result will be the power level in dBm.
Examples (assuming R = 50 Ω):
Q: Why is impedance required for this calculation?
A: Impedance is needed because power depends on both voltage and resistance via the relationship \( P = \frac{V^2}{R} \). Without knowing the impedance, the power (and thus dBm) cannot be determined from voltage alone.
Q: Why is the impedance not allowed to be zero?
A: If impedance is zero, the power calculation would involve division by zero (\( P = \frac{V^2}{0} \)), which is undefined in mathematics.
Q: Can I use this calculator for dBW instead of dBm?
A: No, this calculator is designed for dBm (reference 1 mW). For dBW, the reference power is 1 W, so the formula would be \( \text{dBW} = 10 \cdot \log_{10}\left(\frac{V^2}{R \cdot 1 \, \text{W}}\right) \), which requires a different calculator.
Q: Why does the calculator default to 50 Ω for impedance?
A: 50 Ω is a standard impedance in RF systems, commonly used in antennas, transmission lines, and test equipment. It’s a typical value for many applications, but you can adjust it as needed.
Q: How does impedance affect the dBm value?
A: dBm is inversely proportional to impedance. For a fixed voltage, increasing the impedance (e.g., from 50 Ω to 100 Ω) halves the power (\( P = \frac{V^2}{R} \)), which decreases the dBm value by approximately 3 dB (\( 10 \cdot \log_{10}(0.5) \approx -3 \)).