1. What is a Volts to Electron Volts Calculator?
Definition: This calculator converts electrical potential difference (in volts) to energy (in electron volts) by considering the charge involved, either in coulombs or as a number of elementary charges.
Purpose: It is used in physics and electronics to calculate the energy gained by a charged particle (e.g., an electron) when accelerated through a potential difference, commonly in atomic and nuclear physics.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The energy is calculated using:
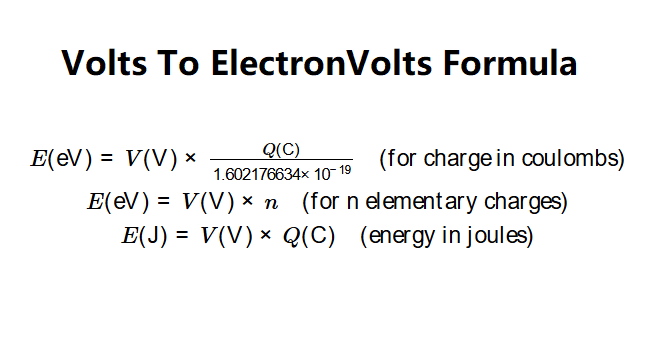
\( E(\text{eV}) = V(\text{V}) \times \frac{Q(\text{C})}{1.602176634 \times 10^{-19}} \quad \text{(for charge in coulombs)} \)
\( E(\text{eV}) = V(\text{V}) \times n \quad \text{(for n elementary charges)} \)
\( E(\text{J}) = V(\text{V}) \times Q(\text{C}) \quad \text{(energy in joules)} \)
Where:
- \( E(\text{eV}) \) is the energy in electron volts (eV)
- \( E(\text{J}) \) is the energy in joules (J)
- \( V(\text{V}) \) is the voltage (Volts, V)
- \( Q(\text{C}) \) is the charge (Coulombs, C)
- \( n \) is the number of elementary charges
- \( 1.602176634 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C} \) is the elementary charge (e)
Steps:
- Enter the voltage (\( V \)) and select a unit (mV, V, kV, MV)
- Select the charge type (Coulombs or Elementary Charges)
- If using coulombs, enter the charge (\( Q \)) and select a unit (pC, nC, µC, mC, C)
- If using elementary charges, enter the number of elementary charges (\( n \))
- Convert voltage to Volts and charge to Coulombs (if applicable)
- Calculate the energy in eV and J using the appropriate formula
Display format:
- If a value is > 10000 or < 0.0001 (and not zero), use scientific notation (e.g., \( 1.23456e-3 \))
- Otherwise, display with 5 decimal places
3. Importance of Volts to Electron Volts Calculation
Details: Converting volts to electron volts is crucial in atomic and nuclear physics, where energy scales are often very small. Electron volts provide a convenient unit for measuring the energy of particles like electrons when they are accelerated through a potential difference.
4. Using the Calculator
Tips: Ensure the charge or number of elementary charges is positive. The calculator handles unit conversions automatically, so select the appropriate units for your values.
Examples:
- Single Electron: \( V = 1 \, \text{V} \), \( n = 1 \, \text{(elementary charge)} \):
- \( E(\text{eV}) = 1 \times 1 = 1.00000 \, \text{eV} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 1 \times 1.602176634 \times 10^{-19} = 1.60218e-19 \, \text{J} \)
- Charge in Coulombs: \( V = 5 \, \text{V} \), \( Q = 1 \, \text{nC} \):
- Convert: \( 1 \, \text{nC} = 1 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{C} \)
- \( E(\text{eV}) = 5 \times \frac{1 \times 10^{-9}}{1.602176634 \times 10^{-19}} = 6.24151e+9 \, \text{eV} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 5 \times 1 \times 10^{-9} = 5.00000e-9 \, \text{J} \)
- High Voltage: \( V = 1 \, \text{kV} \), \( n = 2 \, \text{(elementary charges)} \):
- Convert: \( 1 \, \text{kV} = 1 \times 10^3 \, \text{V} \)
- \( E(\text{eV}) = 1000 \times 2 = 2000.00000 \, \text{eV} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 2000 \times 1.602176634 \times 10^{-19} = 3.20435e-16 \, \text{J} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is an electron volt?
A: An electron volt (eV) is the energy gained by an electron when it is accelerated through a potential difference of 1 volt. It equals \( 1.602176634 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{J} \).
Q: Why use elementary charges?
A: Elementary charges simplify calculations in particle physics, where the charge is often a multiple of the electron’s charge (\( e = 1.602176634 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C} \)).
Q: How is energy in joules related to electron volts?
A: The energy in joules is calculated as \( E(\text{J}) = V(\text{V}) \times Q(\text{C}) \), and in electron volts as \( E(\text{eV}) = E(\text{J}) / (1.602176634 \times 10^{-19}) \).
Volts to Electron Volts Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back