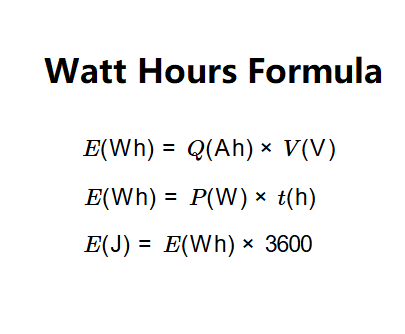1. What is a Watt-Hours Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the energy in watt-hours (Wh), a unit of electrical energy, using either the charge and voltage of a battery, the charge and voltage specifically for watt-hours from amp-hours, or the power and time of a device.
Purpose: It is used to estimate the energy capacity of batteries or the energy consumption of electrical devices, helping in battery sizing, energy management, and cost estimation.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The energy in watt-hours is calculated using:
\( E(\text{Wh}) = Q(\text{Ah}) \times V(\text{V}) \quad \text{(for charge and voltage or watt-hours from amp-hours)} \)
\( E(\text{Wh}) = P(\text{W}) \times t(\text{h}) \quad \text{(for power and time)} \)
\( E(\text{J}) = E(\text{Wh}) \times 3600 \)
Where:
- \( E(\text{Wh}) \) is the energy in watt-hours (Wh)
- \( E(\text{J}) \) is the energy in joules (J)
- \( Q(\text{Ah}) \) is the charge in amp-hours (Ah)
- \( V(\text{V}) \) is the voltage in volts (V)
- \( P(\text{W}) \) is the power in watts (W)
- \( t(\text{h}) \) is the time in hours (h)
Steps:
- Select the calculation type (Charge and Voltage, Watt-Hours from Amp-Hours, or Power and Time)
- For Charge and Voltage or Watt-Hours from Amp-Hours:
- Enter the charge (\( Q \)) and select a unit (mAh, Ah)
- Enter the voltage (\( V \)) and select a unit (mV, V, kV, MV)
- Convert charge to Ah and voltage to V
- Calculate energy using \( E(\text{Wh}) = Q \times V \)
- For Power and Time:
- Enter the power (\( P \)) and select a unit (mW, W, kW, MW, GW)
- Enter the time (\( t \)) and select a unit (seconds, minutes, hours)
- Convert power to W and time to h
- Calculate energy using \( E(\text{Wh}) = P \times t \)
- Convert energy to joules using \( E(\text{J}) = E(\text{Wh}) \times 3600 \)
Display format:
- If a value is > 10000 or < 0.0001 (and not zero), use scientific notation (e.g., \( 1.23456e-3 \))
- Otherwise, display with 5 decimal places
3. Importance of Watt-Hours Calculation
Details: Watt-hours are a standard unit for measuring electrical energy, used to compare battery capacities, estimate device runtime, and calculate electricity costs. This helps in designing efficient systems and managing energy consumption.
4. Using the Calculator
Tips: Ensure all inputs are positive. For battery calculations, use the nominal voltage and rated capacity. For device consumption, use the average power and actual usage time.
Examples:
- Watt-Hours from Amp-Hours: \( Q = 2 \, \text{Ah} \), \( V = 25 \, \text{V} \):
- \( E(\text{Wh}) = 2 \times 25 = 50.00000 \, \text{Wh} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 50 \times 3600 = 180000.00000 \, \text{J} \)
- Battery Capacity (Charge and Voltage): \( Q = 1200 \, \text{mAh} \), \( V = 3.7 \, \text{V} \):
- Convert: \( 1200 \, \text{mAh} = 1.2 \, \text{Ah} \)
- \( E(\text{Wh}) = 1.2 \times 3.7 = 4.44000 \, \text{Wh} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 4.44 \times 3600 = 15984.00000 \, \text{J} \)
- Device Consumption (Power and Time): \( P = 60 \, \text{W} \), \( t = 2 \, \text{h} \):
- \( E(\text{Wh}) = 60 \times 2 = 120.00000 \, \text{Wh} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 120 \times 3600 = 432000.00000 \, \text{J} \)
- High-Power Device (Power and Time): \( P = 1.5 \, \text{kW} \), \( t = 30 \, \text{min} \):
- Convert: \( 1.5 \, \text{kW} = 1500 \, \text{W} \), \( 30 \, \text{min} = 0.5 \, \text{h} \)
- \( E(\text{Wh}) = 1500 \times 0.5 = 750.00000 \, \text{Wh} \)
- \( E(\text{J}) = 750 \times 3600 = 2700000.00000 \, \text{J} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a watt-hour?
A: A watt-hour (Wh) is a unit of electrical energy, representing the energy consumed or stored when 1 watt of power is used for 1 hour. It equals 3600 joules.
Q: Why convert amp-hours to watt-hours?
A: Converting amp-hours to watt-hours accounts for the voltage, providing a more accurate measure of energy, especially when comparing batteries with different voltages.
Q: How does voltage affect watt-hours?
A: For a given charge in amp-hours, a higher voltage results in more watt-hours, as energy is the product of charge and voltage.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back