 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the apparent power (\( S \)) in kVA for electrical systems, which represents the total power in an AC circuit, combining both real and reactive power.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to size transformers, generators, and other equipment in single-phase and three-phase power systems.
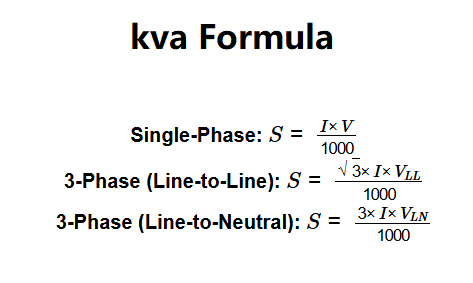
The apparent power is calculated using the following formulas:
Where:
Steps:
Details: kVA is essential for sizing electrical equipment like transformers and generators, ensuring they can handle the total power demand in a system, including both real power (kW) and reactive power (kVAR).
Tips: Input positive values for current and voltage. For three-phase systems, ensure you select the correct voltage type (line-to-line or line-to-neutral) based on your measurement.
Examples:
Q: What is kVA?
A: kVA (kilo-volt-amperes) is the apparent power in an AC circuit, representing the total power (real and reactive) delivered to the system.
Q: What’s the difference between line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltage?
A: Line-to-line voltage (\( V_{LL} \)) is the voltage between two phases in a three-phase system, while line-to-neutral voltage (\( V_{LN} \)) is the voltage between one phase and the neutral.
Q: Why is kVA important?
A: kVA determines the capacity of electrical equipment like transformers and generators, ensuring they can handle the total power demand.